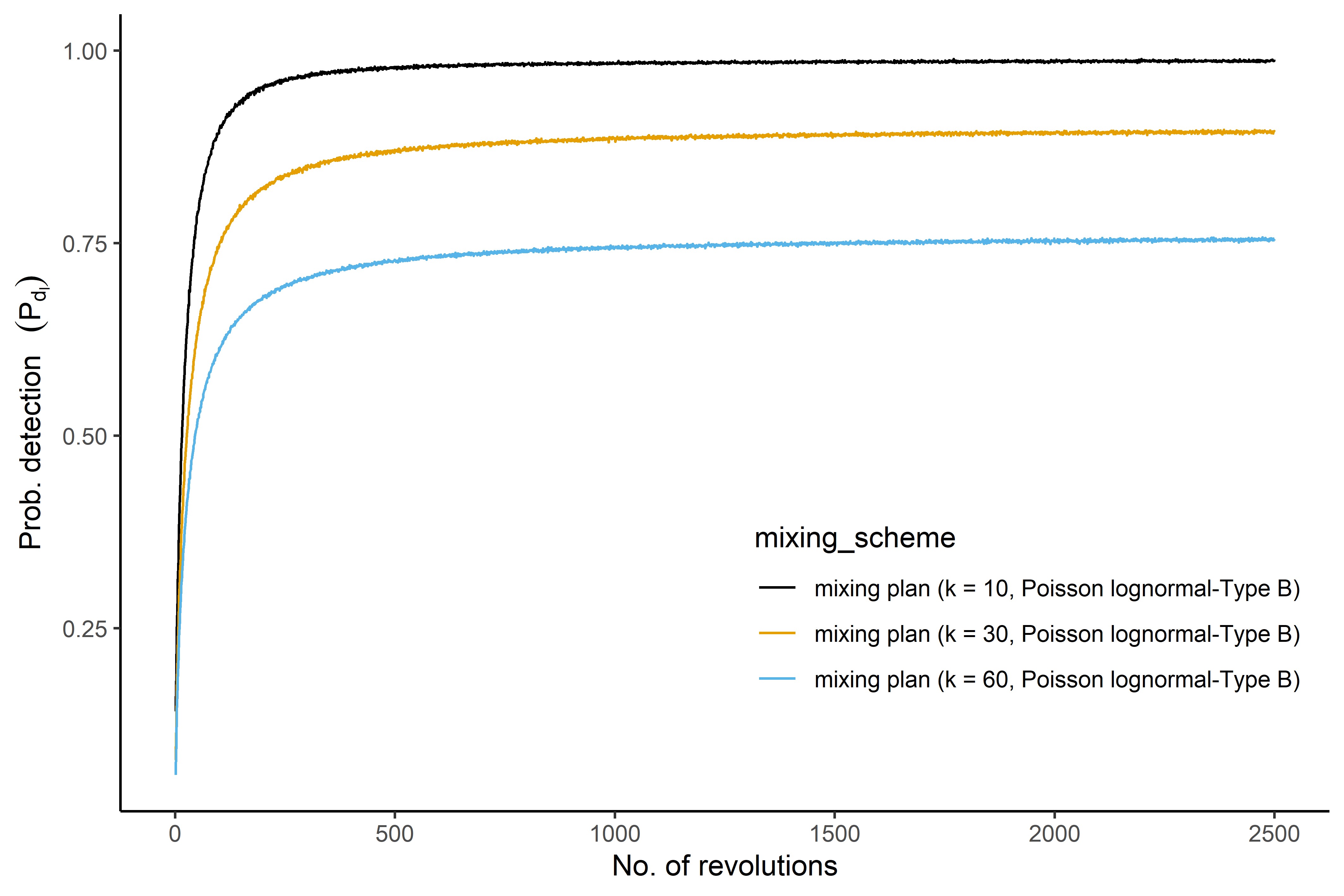
Graphical comparison of mixing plans based on the estimated detection probability at each revolution.
Source:R/compare_mixing_1.R
compare_mixing_1.RdThis function provides a graphical display to compare mixing plans based on the estimated detection probability at each revolution of the mixing process.
compare_mixing_1(mu, sigma, alpha_in, k, l, r, distribution, UDL, n_sim)Arguments
- mu
the average number of CFUs (\(\mu\)) in the mixed sample, which is in a logarithmic scale if we use a Lognormal / Poisson lognormal distribution
- sigma
the standard deviation of the colony-forming units (CFUs) in the mixed sample on the logarithmic scale (default value 0.8)
- alpha_in
concentration parameter at the initial stage
- k
number of small portions / primary samples
- l
number of revolutions / stages
- r
the rate of the concentration parameter changes at each mixing stage
- distribution
what suitable distribution type we have employed for simulation such as
"Poisson-Type A"or"Poisson-Type B"or"Lognormal-Type A"or"Lognormal-Type B"or"Poisson lognormal-Type A"or"Poisson lognormal-Type B"- UDL
the upper decision limit, which depends on the type of microorganisms and testing regulations.
- n_sim
number of simulations
Value
graphical display of estimated detection probability at each revolution in the mixing.
References
Nauta, M.J., 2005. Microbiological risk assessment models for partitioning and mixing during food handling. International Journal of Food Microbiology 100, 311-322.
See also
Examples
mu <- 100
sigma <- 0.8
alpha_in <- 0.01
k <- c(10,30,60)
l <- 2500
r <- 0.01
distribution <- "Poisson lognormal-Type B"
UDL <- 0
n_sim <- 2000
compare_mixing_1(mu,sigma , alpha_in, k, l, r, distribution, UDL, n_sim)